Imaging Services at Sarah D. Culbertson Memorial Hospital incorporates state-of-the-art imaging in a personalized and friendly environment.
We have continually invested in the best diagnostic imaging equipment to ensure we provide the communities we serve cutting-edge technology. We employ only board-certified technologists to perform your comprehensive diagnostic services. The Imaging Department offers immediate appointment availability, high-resolution images, and quick report turnaround, so patients get their results faster. In order to have your diagnostic testing done at Culbertson Memorial Hospital, you will need a signed order from your provider.
How Our Tests Are Read
All of Culbertson Memorial Hospital’s diagnostic imaging tests are read by a premier group of Radiologists. Clinical Radiologists, S.C. (CRSC), is based in Springfield, Illinois, with more than 75 board-certified physicians covering all radiology sub-specialties. CRSC is one of the largest and most progressive radiology groups in not only Illinois but according to Radiology Business Journal, the United States. CRSC provides service to patients in a variety of settings, including -- tertiary, community, and critical access hospitals; multi-specialty and single-specialty clinics as well as physician offices.
CRSC maintains a team of skilled radiologists with many years of experience working with physicians across multiple disciplines. Their radiologists deliver quality interpretations for referring physicians and their patients. CRSC has general diagnostic as well as fellowship-trained physicians, specializing in all areas of radiology, including-- CT; MRI; Ultrasound; Nuclear Medicine; Interventional Radiology; Pediatric Radiology; Neuroradiology; Musculoskeletal; Cross-Sectional Imaging; and Breast Imaging.
For more information or to schedule an appointment for your diagnostic testing with the Imaging Department, please call (217) 322-4321, ext. 5279.
The Following Tests Are Offered At Culbertson Memorial Hospital:
CT Scan
A computed tomography system (CT Scan) provides highly detailed images of the human body in a much faster time, reducing the patient’s time in the scanner. This diagnostic test allows doctors to simultaneously capture multiple wafer-thin images of a patient’s anatomy within seconds. It provides exceptionally high-resolution images that help doctors to more accurately diagnose patients than ever before.
A CT scan can be used to study any body organ, such as the liver, pancreas, intestines, kidneys, adrenal glands, lungs, and heart. It also can study blood vessels, bones, and the spinal cord.
An iodine dye (contrast material) is often used to make structures and organs easier to see on the CT pictures. The dye may be used to check blood flow, find tumors, and look for other problems. Dye can be put in a vein (IV) in your arm, or you may drink the dye for some tests. CT pictures may be taken before and after the dye is used.
3-D Mammography
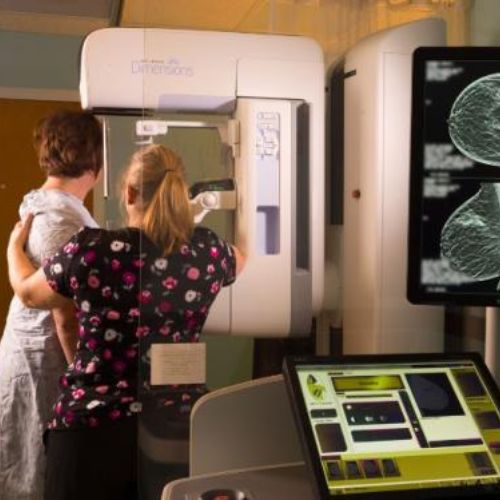
Digital breast tomosynthesis (tomo), also known as 3D mammography, is a revolutionary new screening and diagnostic breast imaging tool to improve the early detection of breast cancer. During the 3D part of the exam, an x-ray arm sweeps over the breast, taking multiple images in seconds. Images are displayed as a series of thin slices that can be viewed by our radiologists as individual images or in a dynamic interactive animation. Approved as an imaging modality by the FDA in early 2011, 3D mammography is used in combination with 2D digital mammography.
Our mammography department is an FDA/IEMA and ACR certified facility. Culbertson Memorial Hospital employs three registered technologists with many years of experience in breast imaging. All mammograms are interpreted by board-certified radiologists who specialize in breast imaging.
We are so proud of our new equipment and the new beautiful mammogram suite we now offer our patients.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging. Unlike X-ray, there is no radiation involved. MRI uses a very strong magnet to produce images of the body in slices, much like a CAT scan. MRI generates highly detailed, cross-sectional images of soft-tissue structures near and around bones, blood vessels, organs, and the brain. This unique technology gives a remarkable window to the internal structure of the body and is capable of revealing even the most subtle differences in body tissues.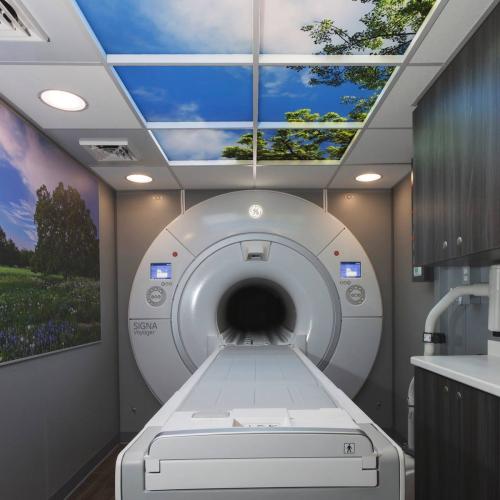
Technology Meets Comfort
Culbertson Memorial Hospital has just added the Signa Voyager MR System from GE Healthcare. This system was designed to help maximize comfort for patients with:
- A 70cm wide bore for more space around you
- Next generation clinical applications designed to reduce exam time
- Quiet Technology to reduce acoustic noise
In addition, this new system delivers uncompromised Imaging capability to help your physician make a definitive diagnosis. Experience the balance of advanced technology and comfort during your next MRI exam.
The MRI mobile unit visits Culbertson Memorial Hospital every Wednesday and Saturday. To schedule an appointment, please call Culbertson at (217) 322-4321, ext. 5271.
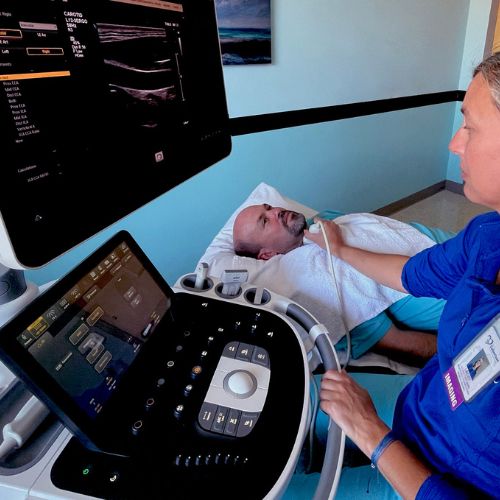
Ultrasound
Ultrasound utilizes high-frequency sound waves to obtain images from inside the body. Ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation; therefore, it is not harmful to the body.
For ultrasound testing, gel or oil is applied to the skin to help transmit the sound waves. A small, handheld instrument called a transducer is passed back and forth over the area of the body that is being examined. The transducer sends out high-pitched sound waves (above the range of human hearing) that are reflected back to the transducer. A computer analyzes the sound waves and converts them into a picture that is displayed on a TV screen. Ultrasound is most useful for looking at organs and structures that are either uniform and solid (such as the liver) or fluid-filled (such as the gallbladder). Mineralized structures (such as bones) or air-filled organs (such as the lungs) do not show up well on a sonogram.
 Doppler Ultrasound
Doppler Ultrasound
A Doppler ultrasound test uses reflected sound waves to evaluate blood as it flows through a blood vessel. It helps doctors evaluate blood flow through the major arteries and veins of the arms, legs, and neck. It can show blocked or reduced blood flow through narrowing in the major arteries of the neck that could cause a stroke. It also can reveal blood clots in legs that could break loose and block blood flow to the lungs.
During a Doppler ultrasound, a handheld instrument (transducer) is passed lightly over the skin above a blood vessel. The transducer sends and receives sound waves that are amplified through a microphone. The sound waves bounce off solid objects, including blood cells. The movement of blood cells causes a change in pitch of the reflected sound waves (called the Doppler effect). If there is no blood flow, the pitch does not change. Information from the reflected sound waves can be processed by a computer to provide graphs or pictures that represent the flow of blood through the blood vessels. These graphs or pictures can be saved for future review or evaluation.
X-ray
X-ray is a painless exam that helps the radiologist diagnose and treat a variety of medical conditions. Images can be taken of the spine, foot, ankle, leg, arm, wrist, hand, chest, abdomen or pelvis.
X-ray is commonly used to:
- Determine whether a bone has been fractured or if a joint is dislocated
- Ensure a fracture has been properly aligned and stabilized for healing
- Guide orthopedic surgery
- Assist in the detection and diagnosis of cancer
- Locate foreign objects
- Evaluate heart and lung status
